As far as conservation of resources is concerned, sustainability is not limited to production and processing alone. voestalpine undertakes numerous activities to optimize the durability of its products as well as their reusability/recyclability/recover-ability.
Due to their ingredients, many of the by-products generated by the production and downstream processing of pig iron and steel can be utilized in-house as recycled materials or in other industrial branches (e.g., steel mill dust in the zinc industry) as secondary raw materials.
Process management in integrated metallurgical facilities is optimized on an ongoing basis in order to ensure a high degree of internal recycling and external utilization of waste and residual products that accrue from production facilities and downstream machinery, including filter dust and mill scale. Additionally, products, residual materials, and waste that accrue in external production facilities are also utilized in voestalpine production facilities, for example, scrap, plastic pellets, and used oil and grease.
At the production sites in Austria, Germany, Sweden, and Brazil, the percentage of recycled materials of the total material used is 23.7%. Around 40% of the total amount of waste generated is recycled.
Percentage of recycled materials of total materials used
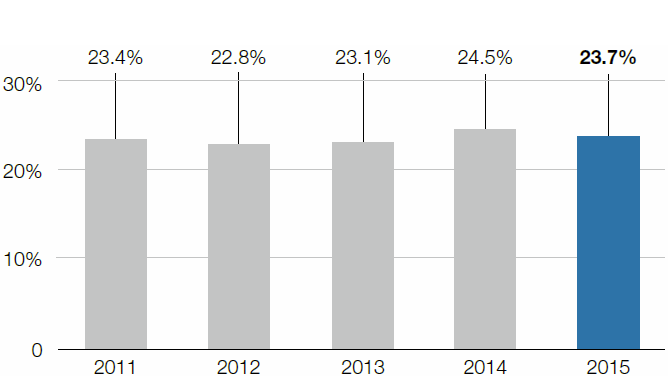
Figures refer to steel production sites in Austria, Germany, Sweden, and Brazil
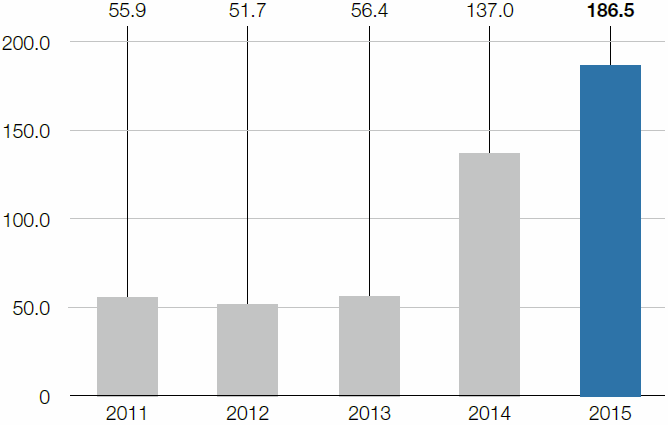
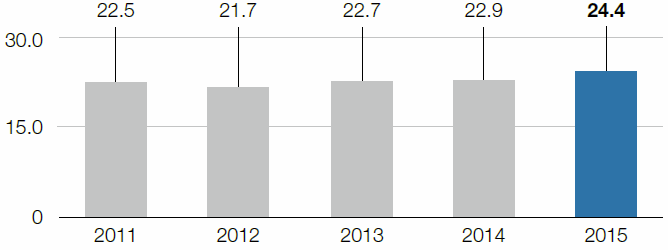
In the 2015 calendar year, the specific volume of non-hazardous waste rose to 186.5 kg per ton of crude steel as a result of changes in the statutory framework conditions, especially for LD slag. The specific volume of hazardous waste on the other hand remained constant at 24.4 kg per ton of crude steel.
Specific volume of non-hazardous waste
kg/t of crude steel
Specific volume of hazardous waste
kg/t of crude steel
Böhler Edelstahl GmbH, Germany
In 2015, almost 260 tons of grinding dust and more than 50 tons of flame cutting dust from voestalpine’s own dust extraction systems were used as a secondary raw material in the electric furnace. Previously, abrasive dust had to be disposed of at the plant’s own dump site.
Share page